Cholelithiasis
Cholelithiasis is the medical term for gall stones.
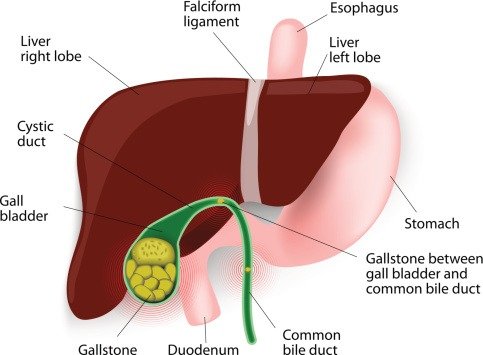
A gall bladder is a pouch-like structure that stores bile produced by the liver that helps indigestion. Wate products like cholesterol and bilirubin are also contained in the bile. Too much cholesterol or too much bilirubin in the bile can lead to gall stone.
Gall stones are hardened deposits of bile that can vary in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball. There can be one single large stone or, multiple tiny stones in the gallbladder.
Types of gallstones:
â— Cholesterol stone: cholesterol stones are the commonest in gall stones. They are made up of hardened cholesterol in the bile that is of yellowish-green color.
â— Pigment stone: pigment stones are made up of bilirubin. Pigment stones are dark in color.
Causes:
â— When the liver produces excessive cholesterol and the gall bladder does not have enough bile salt to dissolve the cholesterol then crystals start to deposit which leads to gall stone.
â— Obesity is another cause.
â— Family history of gallstone.
â— High cholesterol diet.
â— Higher levels of estrogen during pregnancy, history of hormonal therapy.
Symptoms:
â— Biliary colic: sudden onset of pain in the right side of the upper abdomen that lasts for 1 to 5 hours and sometimes for few minutes.
â— Pain can be felt in the center of the abdomen or it can be felt under the right side of ribs that extend to the shoulder blade.
â— Nausea
â— Vomiting
â— Excessive sweating
â— Fever
â— Tachycardia
â— Yellowish discoloration of the skin
â— Itching of the skin â— Cold and shivers â— Loss of appetite
Risk factors:
â— The fatty fertile women age group of 40 are prone. â— Obesity with a cholesterol-rich diet.
â— Alcohol intake
â— Pregnant woman
â— Women with a history of hormonal therapy.
â— Higher intake of antibiotics.
â— Instant weight loss due to dieting or weight loss.
Complications:
â— Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gall bladder. â— Blockage of the bile duct or cholangitis.
â— Blockage of the pancreatic duct.
â— Gallbladder cancer.
Diagnosis:
â— Physical examination: to see the inflammation or tenderness of the abdomen.
â— Endoscopic ultrasound: to see the gall stone
â— Ultrasound of the abdomen: most commonly used to see the signs of gallstones.
â— Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan (HIDA): it is used to diagnose the problem in the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
â— MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography): it is used to see the bile duct or pancreatic duct.
â— ERCP ( endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography):
â— Blood tests to see the infection, jaundice, or pancreatitis.
Homeopathy medicines:
1. Fel Tauri: Fel Tauri is madeup from ox bile. It is well-indicated medicine for gallstone and obstruction of the bile duct. It helps in liquifying the bile and acts as a
purgative and cholagogues. Chronic gastric and intestinal catarrh. Much flatus and ascites.
Boldo fragrans: Boldo fragrans is well-indicated medicine for gallstone with cholecystitis. There is a bitter taste in the mouth with a loss of appetite. Burning pain in the right side of the abdomen. Constipation.
Berberis vulgaris: Berberis vulgaris is good medicine for gallstones. There is a sharp pain in the region of the gallbladder, worse when applying pressure, and then extends to the stomach. Gallstones attacks with severe pain. Catarrh of the gallbladder with constipation and yellowish discoloration of the skin.
Chionanthus Virginica: this is well-marked medicine for gallstone or biliary colic. Tenderness of the right side of the abdomen. Cholecystitis. Constipation with clay-colored stool. Jaundice with the arrest of menses.