Cirrhosis Of Liver
Introduction: cirrhosis is a late stage of the liver disease in which healthy liver tissues are replaced with scar tissue and the liver is permanently damaged.
Cirrhosis always develops because of another liver problem . Its condition in which the liver does not function properly due to long term damage in the cells of the liver.
Cirrhosis is most commonly caused by alcohol, hepatitis B, hepatitis-c or non alcoholic drinks per day over a number of years is required for alcoholic cirrhosis to occur.
It progresses gradually in years and if left untreated, buildup of scars tissues can eventually stop liver function.
Causes:
Cirrhosis is the complication of the fatty liver and hepatitis B or C.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Hepatitis B or C.
- Primary biliary cholangitis.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Biliary atresia, poor formed bile duct.
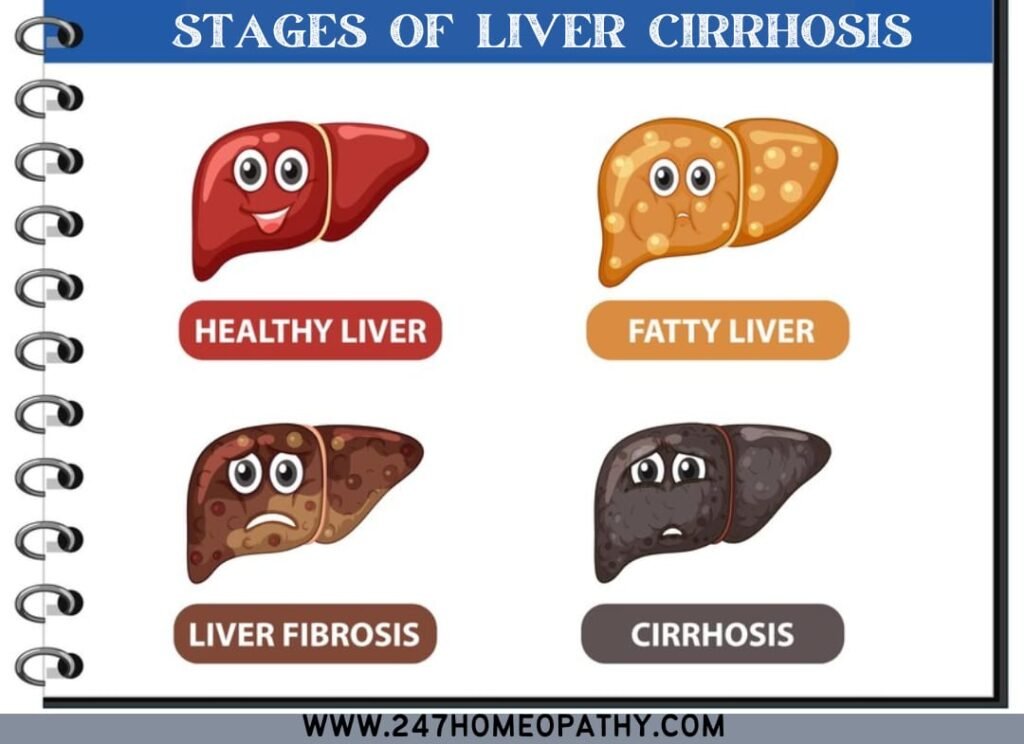
Stages of Liver Cirrhosis:
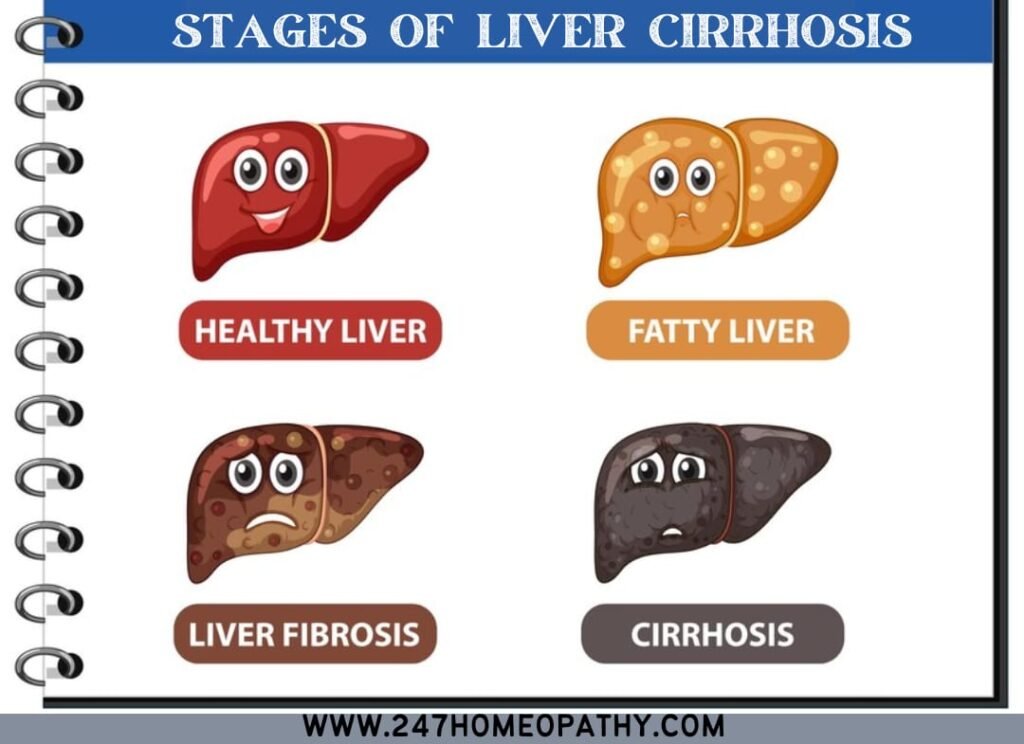
Stage 1: mild inflammation with minimal effect on liver functions.
Stage 2: Accumulation of scar tissues with normal liver functions.
Stage 3: Fibrosis and scarring of the liver.
Stage 4: Complete damage of the liver cells with
Impairing Vital Functions Symptoms:
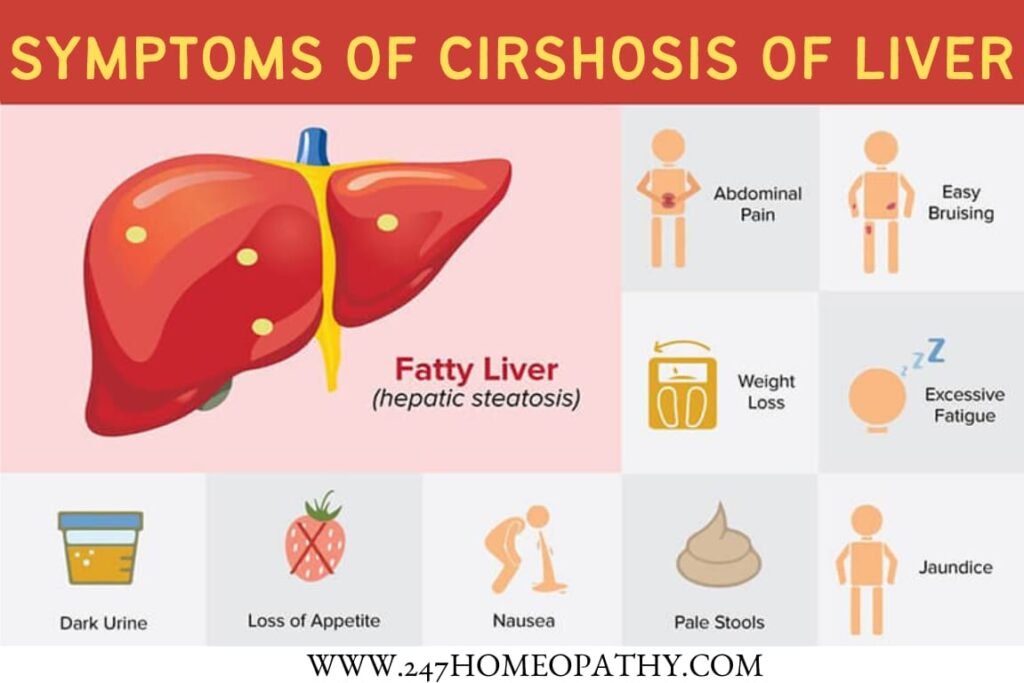
Liver Size Can Be Enlarged, Normal or Shrunken on People with Cirrhosis.
In The beginning, It may not cause any problems but as time passes an individual may notice symptoms like:
- Weakness or fatigue
- Nausea.
- Loss of appetite.
- Swelling in the legs and feet.
- Weight loss.
- Yellowish discoloration of the Skin and Conjunctiva.
- Fluid accumulation in the abdomen ( ascites).
- Itchy skin.
- Spider nevi – blood vessels get prominent and
- look like spider webs.
Palmar Erythema : Redness of the hypothenar and thenar eminences of the palm.
- Hypogonadism in both male and females.
- Portal hypertension.
- Drowsiness and slurred speech.
- Enlargement of a spleen in advanced stages.
Diagnosis:
Laboratory Test:
1. AST and ALT.
2. Alkaline phosphatase.
3. Bilirubin.
4. Albumin.
5. Globulins.
6. Immunoglobulin Levels- IgE , IgM, IgA.
- Ultrasound.
- CT- scan.
- Biopsy.
- Fibroscan.
Preventions:
1. Avoid alcohol.
2. Eat a healthy diet.
3. Maintain a healthy diet.
4. Reduce risk of hepatitis.
5. Reduce salt intake.
6. Low sodium diet should be taken. 7. Maintain glucose level.
Homeopathy Treatment :
Treatment at Dr Chhabra’s not only helps in improving the functions of the liver it also controls the size of liver and prevents scarring of the liver.
Treatment at Dr Chhabra’s is tailored according to the patient’s condition. Not only the physical conditions are kept in mind but psychological factors such as anxiety, stress, emotional factors are considered for selection of medicines.