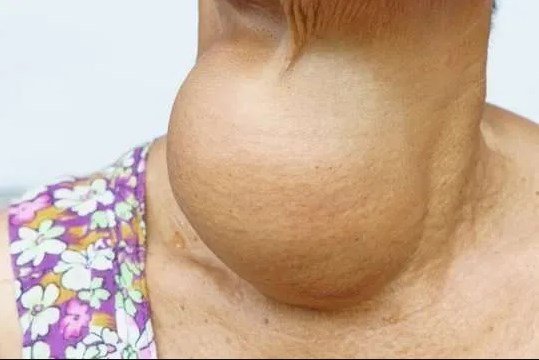
Goitre
Goitre is the medical term for the enlarged thyroid gland.
Abnormal expansion or growth of the thyroid gland is known as goitre.
It commonly occurs due to iodine deficiency that causes inflammation of the thyroid gland.
The thyroid gland releases the hormones names thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) that plays a major role in the metabolic system, mood or emotions, heart rate etc.
Goitre more commonly affects women of the age group of 40 or above 40 years as compared to men.
What Causes Goitre:
• Grave’s disease: grave’s disease is an autoimmune disease where the immune system of the body attacks the thyroid gland and causes enlargement of the thyroid gland.
• Hashimoto’s disease: it is also an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the thyroid gland and produces little hormones and then gets better by itself
• Thyroid cancer: thyroid can cause the abnormal growth of the thyroid gland.
• Thyroiditis: infection of the thyroid gland caused by bacterias and viruses.
Nodules: fluid-filled cysts and lumps on the thyroid can cause goitre.
• Pregnancy or menopause can be the reason for thyroid enlargement.
• Hereditary: people with a family history of goitre are at higher risk of getting goitre
Types of goitre:
1. Simple goitre: simple goitre means when the thyroid gland can not make enough hormones and to full fill, the crisis thyroid gland grows larger to make enough hormones.
2. Colloid goitre: also known as endemic goitre. This is caused by lodine deficiency in the diet.
3. Non-toxic goitre: non-toxic goitre is mainly caused by certain medications like lithium for mood disorders and amiodarone for irregular heartbeat can trigger the abnormal growth of the thyroid gland.
4. Multinodular goitre: when multiple nodules or lumps appear over the thyroid gland called a multinodular goitre.
Toxic goitre is accompanied by hyperthyroidism where the thyroid gland produces excessive thyroid hormones.
Symptoms of goitre:
• The swollen and enlarged neck is a visible sign.
• Difficulty in eating and drinking
• Difficulty in breathing.
• Hoarseness of voice.
• Coughing.
• Tightness of the throat.
Toxic goitre with hyperthyroidism can cause:
• Tachycardia
• Loose stool
• Increased perspiration
• Trembling
• Increased metabolic rate can lead to weight loss.
In hypothyroidism:
• Metabolic rate get decreased
• Gaining weight.
• Irregular menstrual cycle
• Constipation
• Dry skin
Complications of goitre:
• Patients with the autoimmune condition of thyroid can form lymphoma in later stages. The enlarged thyroid gland can cause compression to a nearly situated structure that can cause difficulty in breathing, eating or drinking etc.
• Thyroid abscess
• Haemorrhage from nodular goitre.
Diagnosis:
1. Ultrasound: to the size, shape of gland or presence of nodules.
2. TSH test: to see the parameters of T3 and T4.
3. Radioactive iodine scan: radioactive iodine inserted into the gland to the detailed picture of the thyroid gland.
4. FNAC: biopsy if suspecting cancer of thyroid gland.
Homeopathy management:
1. lodum: iodum is well-indicated medicine for hyperthyroidism where the thyroid gland produced excessive hormones that cause an increased metabolic rate and weight loss even if the patient is taking a good diet. The patient is restless and feels hot flushes in the body. Anxiety with tachycardia. Hoarseness of voice, bulging out of eyeballs with chronic diarrhea can be
there.
2. Conium maculatum: it works well in the enlarged thyroid gland of the patient with depression. A person with depression who has lost interest in his or her work. The patient is very irritable with weak memory. Excessive perspiration on the hands. It can be given in women with hyperthyroidism when there is an irregular menstrual cycle.
3. Natrum muriaticum: natrum muriaticum can be given in exophthalmos goitre. Hypertrophy of tonsils and thyroid gland.
Goitre with a chronic sore throat. Hoarseness of voice in the morning. Voice weak, exhausted from talking. Bad effect of speaking for a longer period.
4. Kali iodatum: kali iodatum is well indicated for thyroid disorder.
There is swelling of the thyroid gland. Hoarseness of voice with pain. Goitre is sensitive to contact.