Diabetes Mellitus
Introduction: it is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disorder of carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism that results from insulin deficiency or abnormality in the use of insulin.
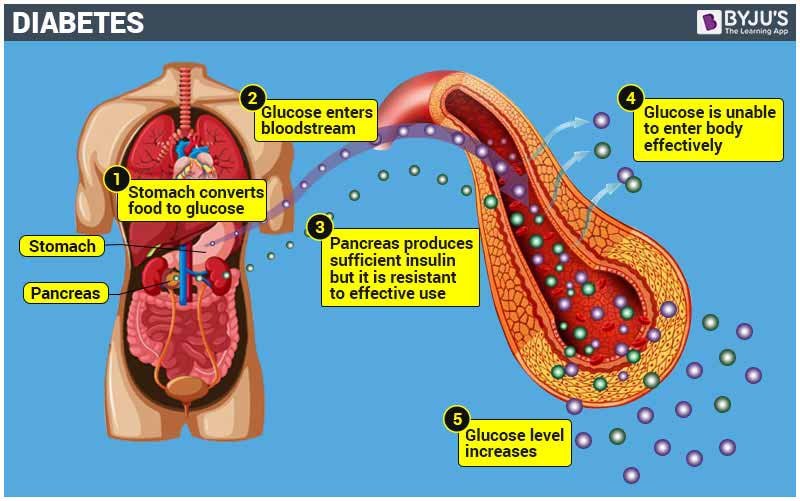
Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced.
It can be characterized into three types:
â— Type 1 diabetes: pancreas fails to produce enough insulin due to the loss of beta cells.
Type 1 diabetes known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. (loss of beta cells is caused by an autoimmune disease.)
â— Type 2 diabetes: it starts with insulin resistance, in type 2 diabetes cells fail to respond to insulin. type 2 diabetes also known as noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
â— Gestational diabetes occurs when pregnant women without a previous history of diabetes develop high blood sugar levels.
Causes:
â— Type 1 diabetes: the exact cause is unknown. But due to
some reason loss of insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas, leads to insulin deficiency. It can occur at any age and is diagnosed during adulthood.
â— Type 2 diabetes: it’s a combination of genetic factors and lifestyle. Obesity can be the cause of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
◠Genetic factors play a major role in this.if a person’s family member like his mother or father is suffering from diabetes, they have higher risk to develop diabetes.
â—
Other risk factors:
â– Hypertension. â–Family history. â–Physical inactivity. â– Obesity.
â–Stress and anxiety, â–Unhealthy food.
Symptoms: (general)
â–Increased thirst .
â–Frequent urination especially at night. â– Pruritus.
â–Increased hunger.
â–Weight loss.
â–Unhealed wounds in advanced cases. â– Weakness.
â–Nausea and vomiting.
â–Blurry vision.
â–High blood pressure.
Symptoms in men’s:
â–Erectile dysfunction. â–Sexual debility decreases. â–Poor muscle strength.
Diagnosis:
â— Blood sugar fasting.
â— HBA1C test.
â— Glucose tolerance test.
Prevention:
â— Do regular exercise.
â— Avoid alcohol.
â— Avoid smoking.
â— Reduce stress.
â— Do regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. â— Maintain weight.
â— Avoid junk food.
â— Decrease sugar intake or carbs in the diet.
Homeopathy treatment:
Homeopathy medicine improves or boosts the immune system.
It can control blood sugar levels.
There are no side effects of homeopathy medicine.