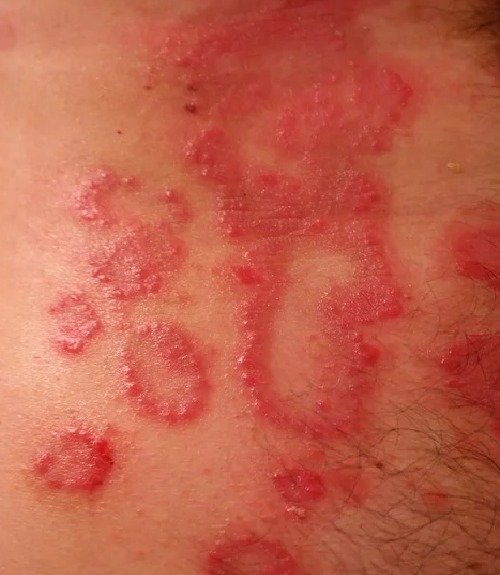
Eczema
Eczema also called atopic dermatitis. It is a condition wherein patches of skin become inflamed, cracked, itchy, and rough.
Commonly seen in babies and young children, appearing on the face of infants. This can come in a variety of types in children, teens, and adults. Eczema is not contagious. The cause is unknown. Caused by both genetic and environmental factors.
It may get better or worse over time, but it is a long-lasting disease. The most common type is atopic dermatitis.
Types of Eczema
1. Atopic dermatitis – It is characterized as dry, itchy skin that often appears with a red rash.
2. Contact dermatitis – It is caused by contact with irritants.
Burning, itching, and redness occur. When the irritant is removed inflammation goes away.
3. Seborrheic dermatitis – This happens in areas of your body with lots of oil glands. When it’s on your scalp it c dandruff.
Causes
The exact cause of eczema is unclear but presumed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
1. It may sometimes be an allergic reaction from house dust mites
2. Food allergies may play a role in causing this
3. Family history of eczema
Common triggers of eczema
• Synthetic fabrics
• Sweating
• Temperature changes
• Food allergies
• stress/anxiety
• Animal danders
• Rough scratchy material
• Woolen clothes
• Chemical uses in detergent that dries out the skin
• Humidity
Symptoms
• Itching, dryness, inflamed, and irritate the skin
• Intense itching
• Small, raised bumps that ooze fluid when scratched
• Thickened scaly skin
• Dry skin
• Itching especially at night
• Redness of skin, swelling
Symptoms in infants
• Rashes on the scalp and cheeks
• Extreme itchiness may interfere with sleeping
Symptom in children
• Bumpy rashes
• Skin thickening
• Rashes that appear behind the creases of elbows or knees
Symptoms in adults
• Very dry skin
• Rashes that cover much of the body
• Skin infections
• The appearance of skin affected by atopic dermatitis will depend on how much a person scratches
Diagnosis
• Physical examination
• Allergy test to look for irritants or triggers
• Patch test
Prevention
• Moisturize your skin
• Avoid sudden change in temperature
• Avoid scratchy material
• Avoid direct skin contact of woolen clothes
• Don’t use harsh soap, detergents
• Pay attention to foods that might trigger symptoms and try to avoid them
• Avoid trigger factors like synthetic fabric
• Avoid scratching to prevent breaking the skin, rub rather than scratching the affected area.
• Cream-based moisturizer or coconut oil that will help soothe your skin
• After your bath, gently blot your skin with a soft, never rub.
• Wear loose-fitting clothes made from soft fabrics like cotton.
Homeopathic medicine
Arsenic Album – Eczema with burning and restlessness. Itching produces burning, worse cold, and cold applications. Its between fingers and cracks on the tip of the fingers. Best normally for chronic eczema if there is great burning and itching. Eczema of the vulva.
Chrysarobinum– Vesicular eruptions associated with a foul-smelling discharge and crust formation. Violent itching of thighs, legs, and ears. Dry scaly eruptions. Eczema behind the ears.
Petroleum – Has yellowish-green thick crusts on the face and neck. On scratching a liquid comes out and often blood.
Eczema disappearing in summer and reappearing in winter.
Eczema with fissures on hands and behind the ears. The discharge is watery. It is especially suitable for eczematous erruptions behind the ears.
Sulphur – Dry rough skin. Much itching. Eczema in the folds of skin. Eczema of the hairy parts. pruritis, worse washing. Bad odor from the body. Eczema caused by the use of hair dyes.
Psorinum – Crusty, scaling, dry eczema of the scalp and face.
Hair falls out. Terrible itching worse from the warmth of the bed.
Oily skin. It is behind the ears and bends of joints with fetid discharge.
Kali Muraticum – Moist eczema. It is especially useful in chronic and obstinate forms of eczema. Vesicles contain a thick white content. Eczema of the face and head of children.